Newton's Second Law of Motion
Newton's Second Law of Motion: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Second Law of Motion, Mathematical Formulation of Second Law of Motion, Impulse of a Force and Rate of Change of Momentum etc.
Important Questions on Newton's Second Law of Motion
In how much time an object having mass of will speed up from if force will be applied to it
When we apply a force of , we can hold a body whose mass is approximately equal to
The change in momentum of a body in is . The force acting on it is
If an object of mass experience a force of , the acceleration produced by it is.
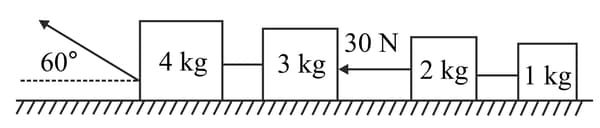
Figure shows four blocks that are pulled along a smooth horizontal surface. The masses of the blocks and tension in one cord are given. The pulling force is
For a body thrown vertically upwards, if the air resistance is taken into consideration, then the time of rise is
A diwali rocket is ejecting of gases per second at a velocity of . The accelerating force on the rocket is
Read the following statements and choose the correct option:
Statement: Newton's second law of motion gives the measurement of force.
Reason: According to Newton's second law of motion, force is directly proportional to the rate of change of momentum.
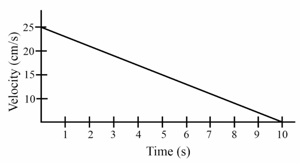
The velocity-time graph of a ball of mass moving along a straight line on a long table is given in figure.The force exerted by the table on the ball to bring it to rest is :
A machine gun fires a bullet of mass gram at a speed of . The man holding it can exert a maximum force of on the gun. How many bullets can he fire per second at the most?
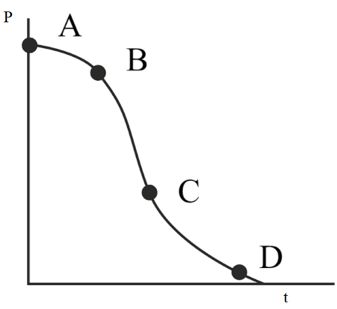
The variation in momentum with time, for a body under collision is shown in figure. The maximum & minimum instantaneous forces are respectively on these points:
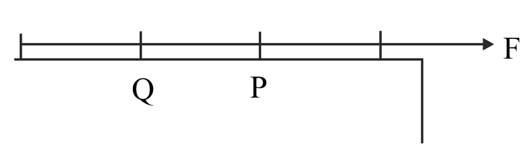
A force ‘F’ is applied on one end of a rope of length ‘a’. P and Q are two points of length ‘b’ from nearest end. The ratio of tensions in string at P & Q is :
An object of mass is moving with an acceleration of . Force acting on the object will be:
In a two body collision, the momentum is varying with time as shown in graph. The instantaneous force is maximum at:
A small block of material having relative density is immersed in a liquid and released. The block starts moving upwards with an acceleration . The value of is :( is the acceleration due to gravity)
A dynamometer D is attached to two masses and . Forces of and are applied to the masses as shown.
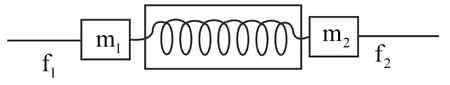
The dynamometer will read :
A particle of mass is subjected to a force with , what will be its acceleration if it is released from a point
State the Newton's second law of motion and explain. Describe the applications of second law of motion in our daily life.
In a rocket of mass fuel is consumed at a rate of . The velocity of the gases ejected from the rocket is . The thrust on the rocket is
